The BGOOD (BGO-Open Dipole) experiment, located at the ELSA electron accelerator of the University of Bonn (Germany), is the result of an international collaboration that includes the participation of INFN (MAMBO-CSN3 project) through several sections and laboratories.
BGOOD is designed to systematically investigate meson photoproduction reactions, both with and without strangeness, with particular focus on t-channel processes at low momentum transfer, and at energies close to the photoproduction threshold. One of its main goals is to study the excitation structure of the nucleon and to identify poorly understood baryon resonances. A key interest is the search for non-conventional baryonic and mesonic states, such as tetraquarks and pentaquarks, i.e., configurations beyond the traditional three-quark model. Such exotic states have already been observed in the charm (c) and bottom (b) quark sectors, but in the strange (s) sector, there remain open questions and intriguing analogies, including possible connections to coherent production on the deuteron, which may indicate the formation of di-baryon states.
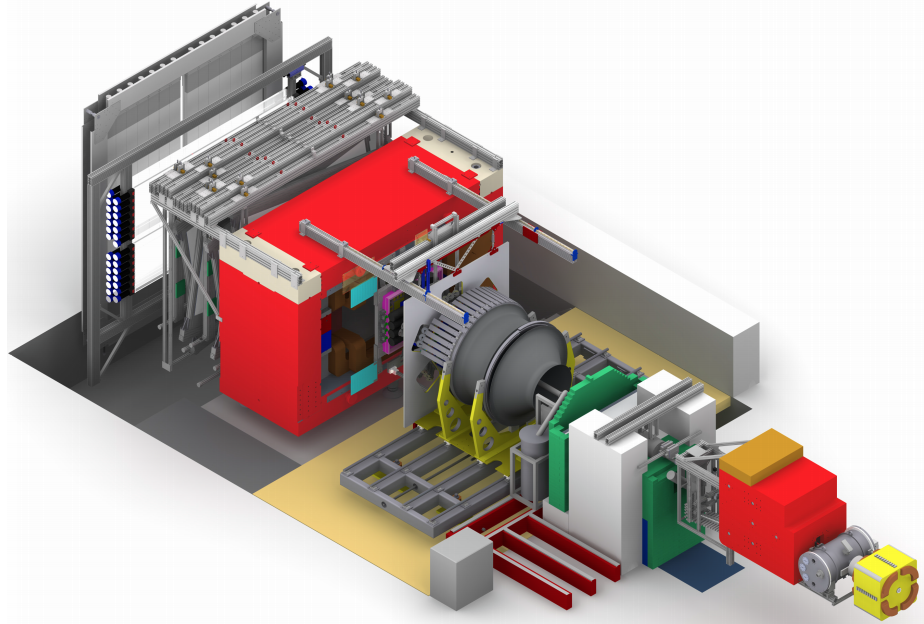
The wide angular coverage and the detector combination of the BGOOD apparatus make it particularly well-suited to explore this still under-investigated sector of low-energy QCD. Another line of research involves beam asymmetry measurements, enabled by the use of linearly polarized photon beams, in the photoproduction of pseudoscalar mesons such as η and η′ on nucleons, which provides a powerful tool to probe the dynamics of baryon resonances and excited nucleon states.
The BGOOD setup uniquely combines a BGO crystal calorimeter, with large solid-angle coverage (nearly 4π) optimised for detecting photons and neutral particles in the central region of the detector, with a forward magnetic spectrometer featuring a dipole magnet, allowing for precise identification and momentum reconstruction of charged particles.
Il setup di BGOOD combina in modo unico un calorimetro a cristalli di BGO, con un’accettanza a grande angolo solido (quasi 4π), ottimizzato per la rivelazione di fotoni e particelle neutre nella regione centrale dell’apparato, con uno spettrometro magnetico anteriore ad ampia apertura, dotato di un dipolo magnetico, che consente la precisa identificazione e misurazione del momento delle particelle cariche.
References
Alessia Fantini
BGOOD experiment